Width as an indicator of health
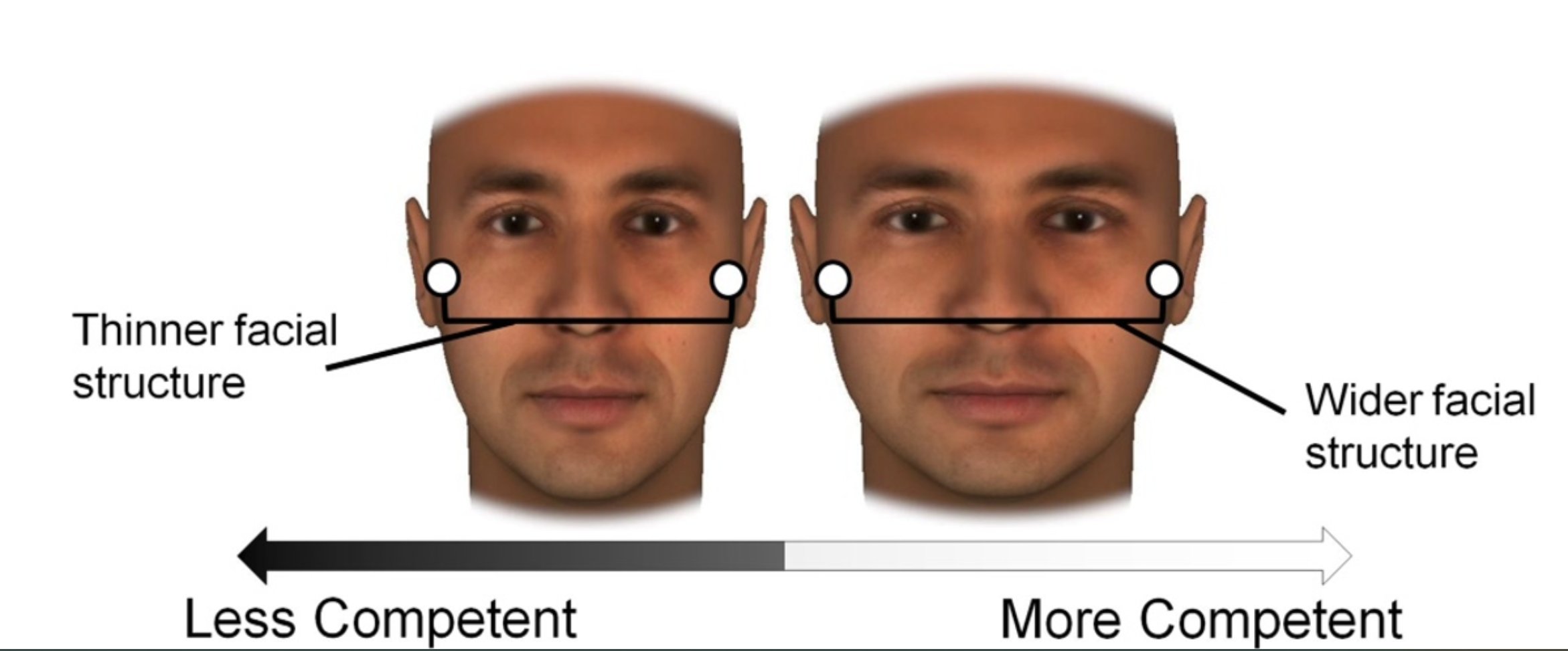
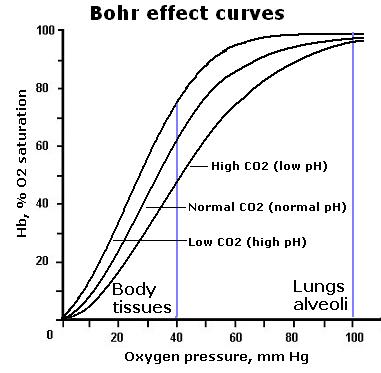
A wide face/skull is universally seen as more attractive than a tall and narrow one. This is not arbitrary and is, in fact, an indicator of one’s ability to retain CO2 --the master molecule of metabolism. A wide face then lends to improved health/life in all facets.
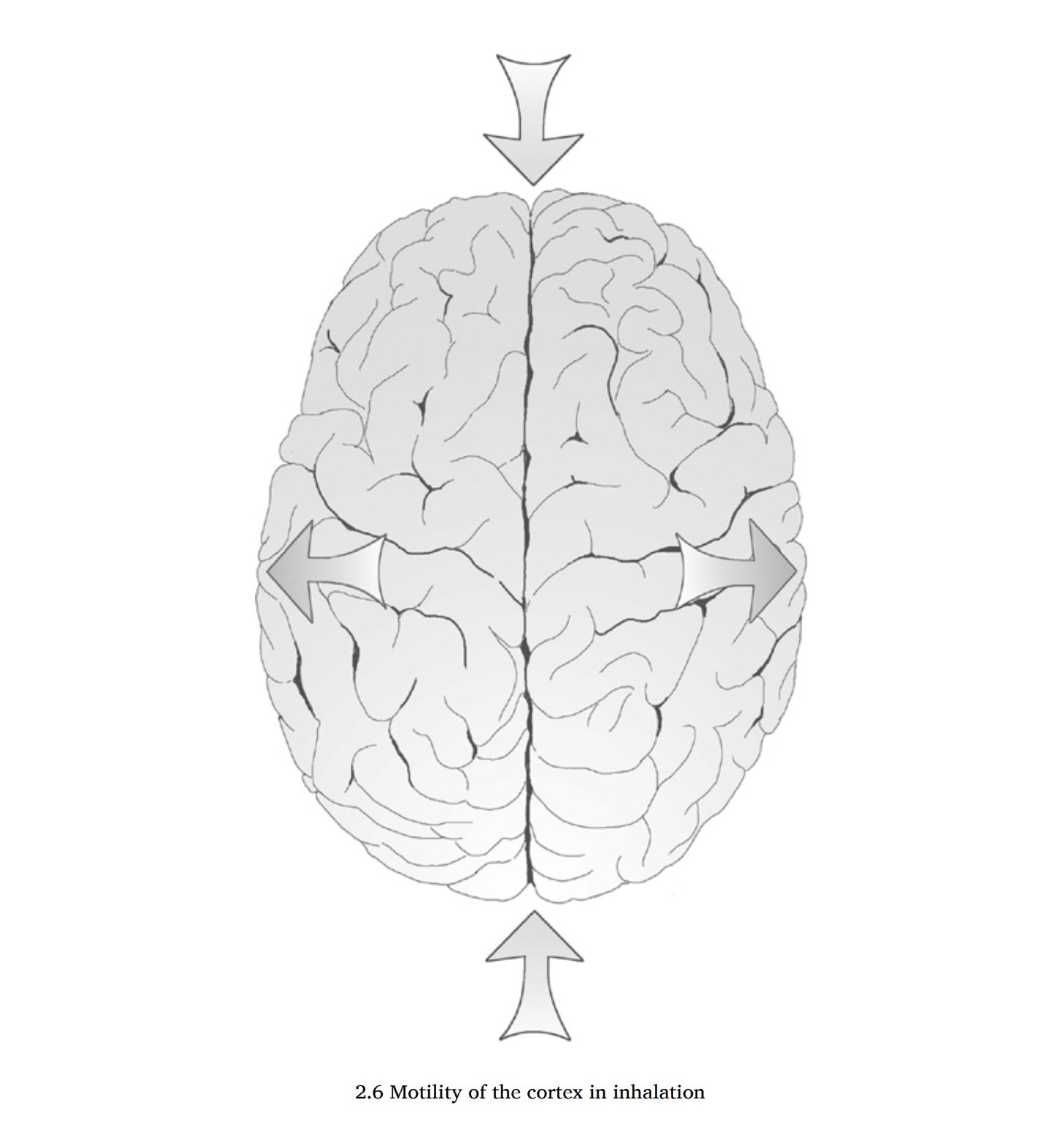
Expansion during inhalation
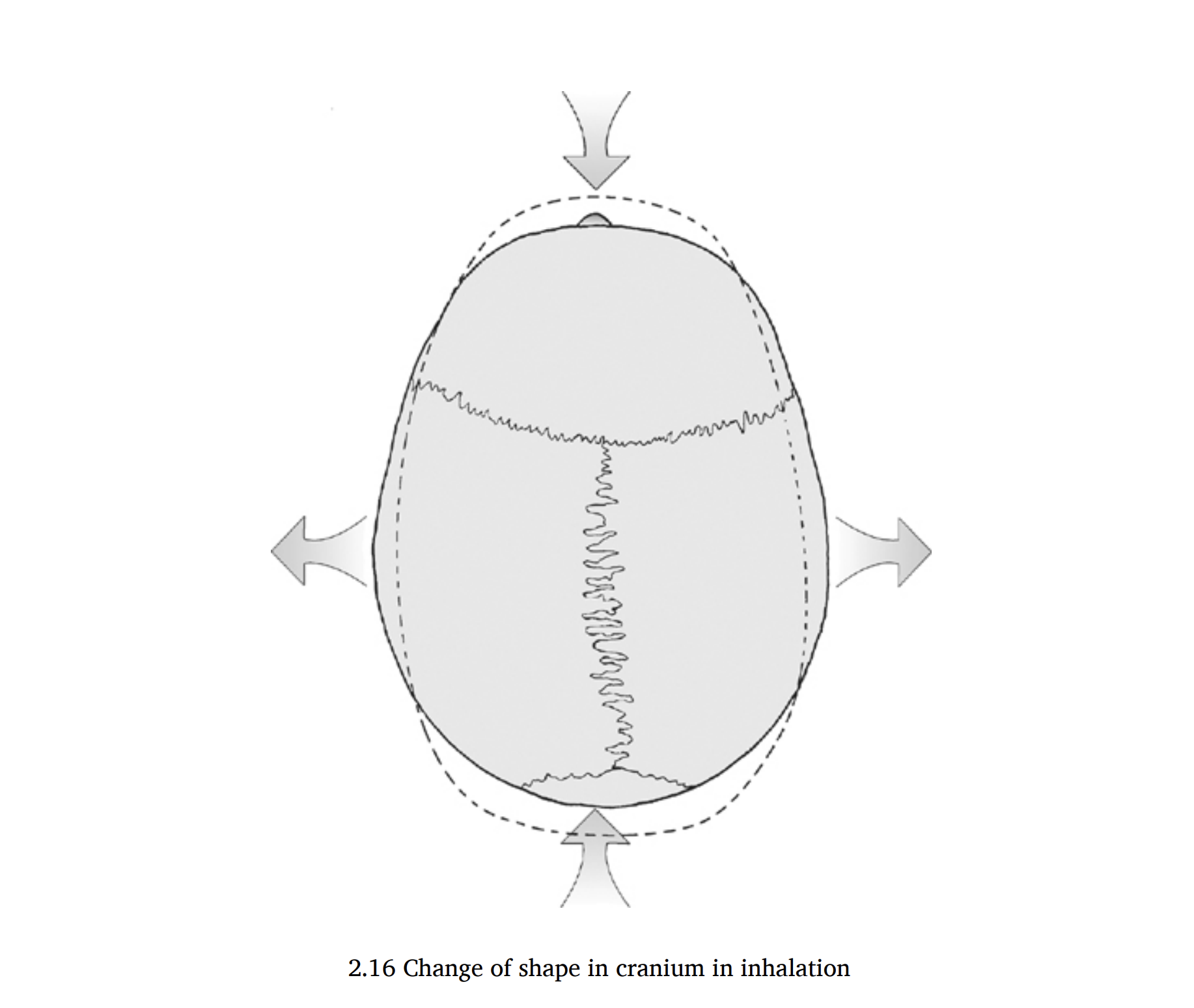
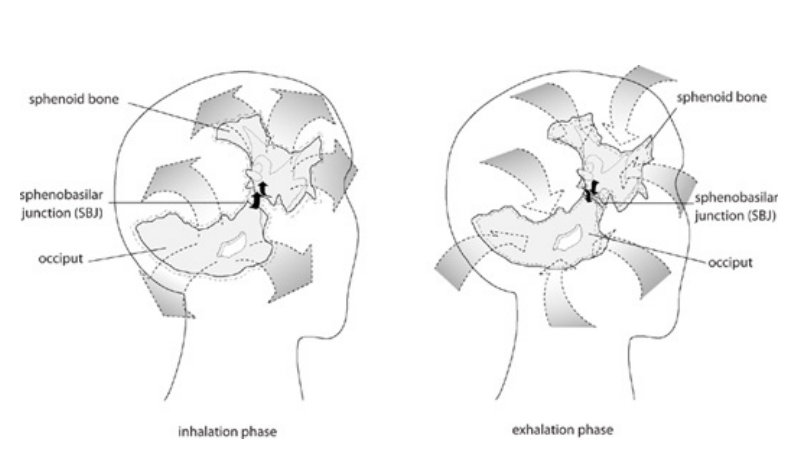
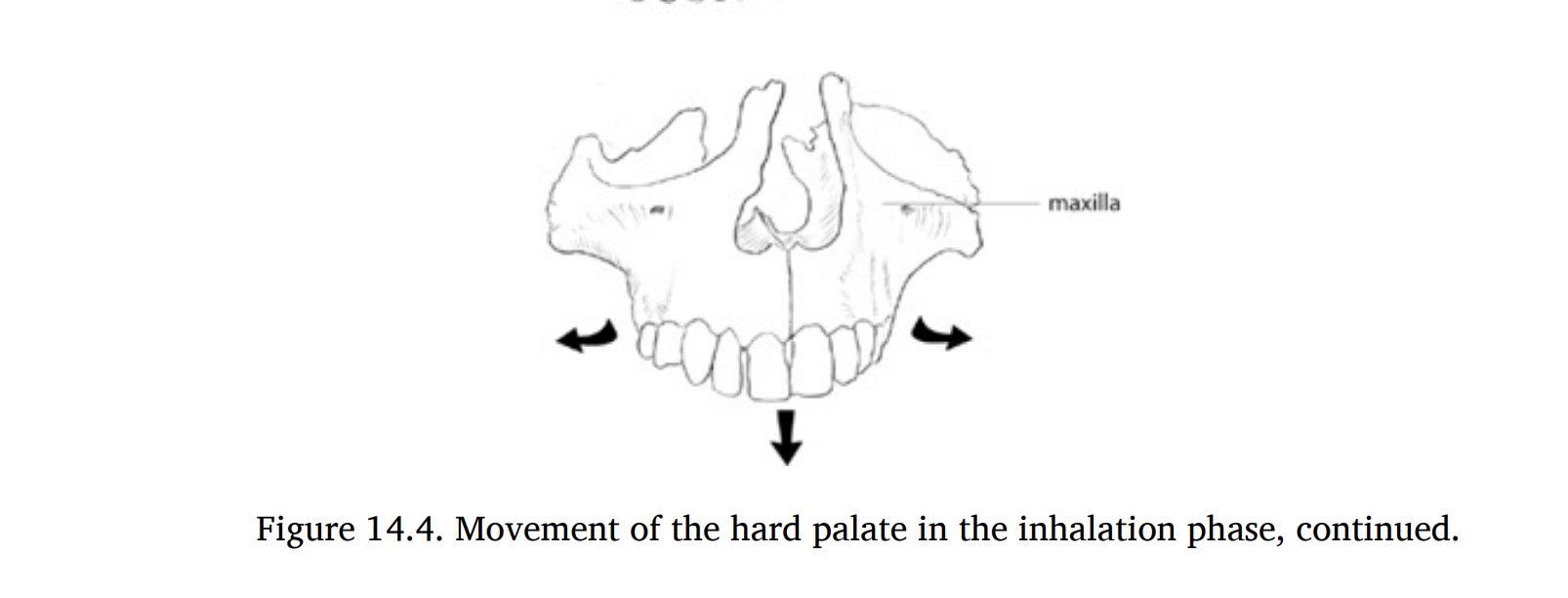
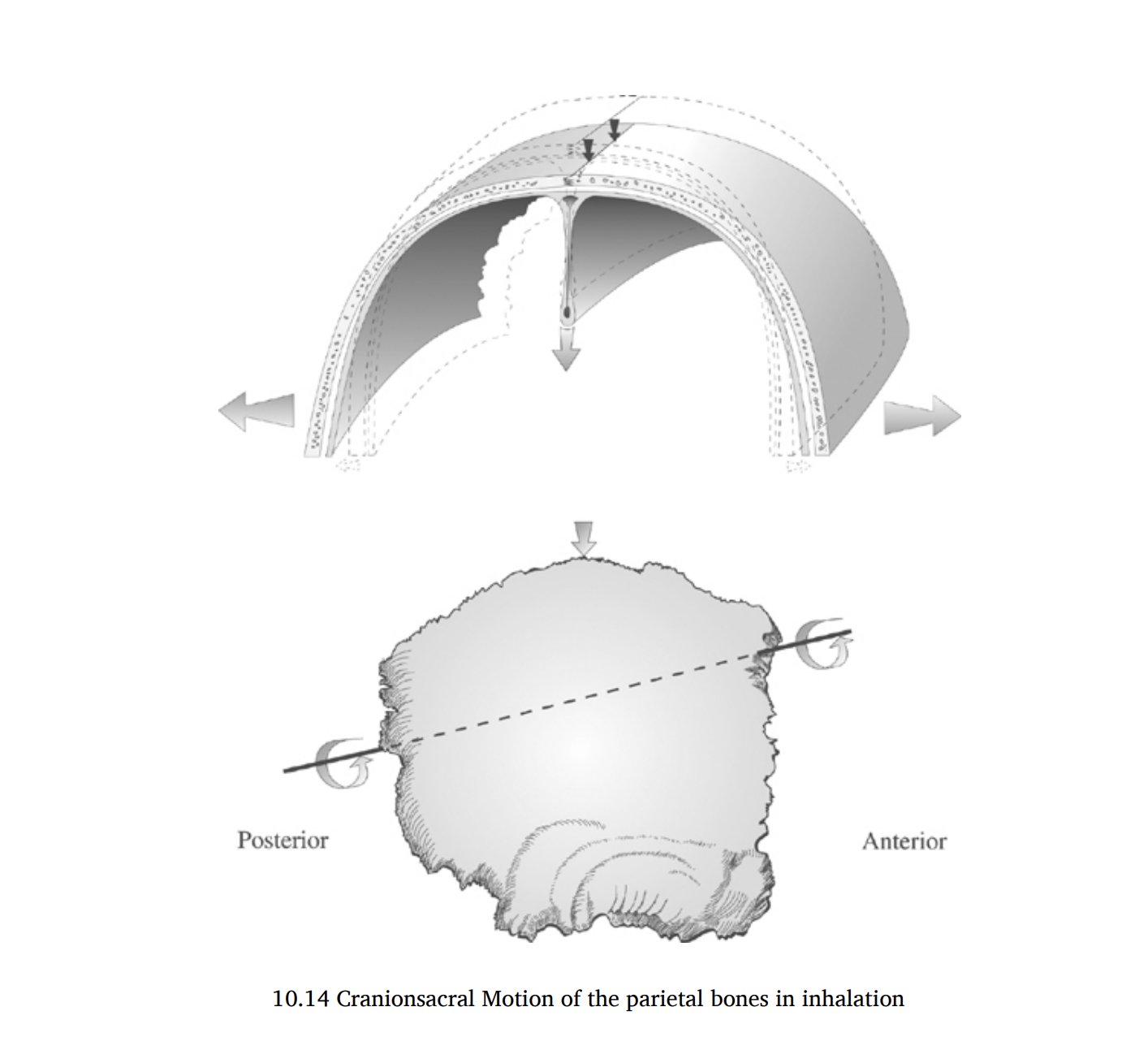
The skull and face expand (widen) during inhalation, drawing the nourishing CSF into the brain. It closes back up (narrows) during the exhale to pump CSF out into the rest of the spine. In time, the skull takes on the shape that it assumes the most.
Craniosacral RhythmForm is function
If the inhale phase is dominant, then the face and skull will reflect this by being short and wide. If the exhale is dominant, the skull will become tall and narrow. This is shaped throughout a lifetime but can be corrected given the right circumstances.
CO2 retention
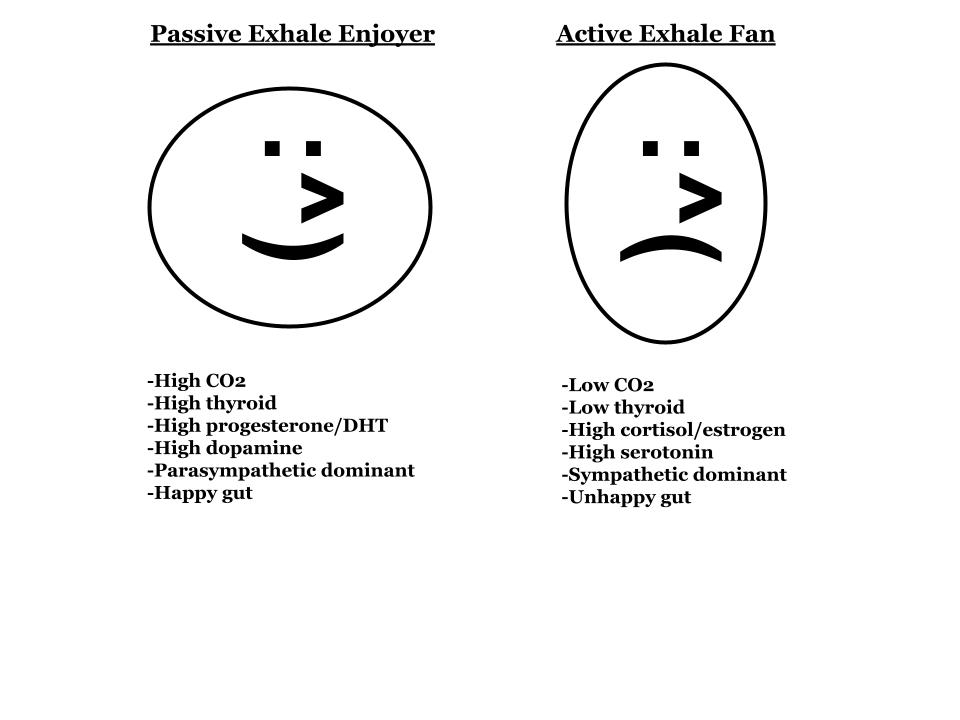
CO2 is retained by limiting the force and extending the duration of the exhale. An active exhale that is short --driven by the contraction of various muscles-- will expel more CO2. Generally, this will take place under stress but can become a chronic habit for some.
Slow, passive, exhales
An ideal exhale is slow and passive, simply the relaxation of the muscles of inhalation. This prevents the loss of CO2, allowing it to perform its many roles including driving oxygen into cells/tissue. Slow breathing rates are a feature of the longest-lived animals on earth.
Constant shaping
By slowing your breathing and relaxing while you exhale you can increase the amount of CO2 you retain and eventually widen your face and skull. This will not happen overnight but will be the result of consistent changes to breathing patterns and other metabolic interventions.
Parietal wings
Additionally, you can feel the movement of the skull each time you breathe. Place your fingers on your parietal bones (above your ears) and they will gently open like wings as you inhale. Conscious recognition of this can potentially lead to greater increases in shape.
Increasing CO2 production
Means to increase CO2 production/retention:
-Relaxing; doing anything you enjoy
-Carbohydrates (sugar)
-Thiamine (and all other B vitamins)
-Thyroid hormones
-Light
-Low-intensity movement
-Magnesium
-Caffeine
-Methylene blue
-Aspirin
-Baking soda
-Pyruvate
Avoid CO2 limiters
Things that oppose CO2 production/retention:
-Any form of stress
-ANS dysfunction
-Misaligned cranial bones/spine
-Darkness
-Parathyroid hormone
-Prolonged high-intensity exercise
-Excessive fatty acid oxidation
-PUFAs (from seed oils)
-Endotoxin