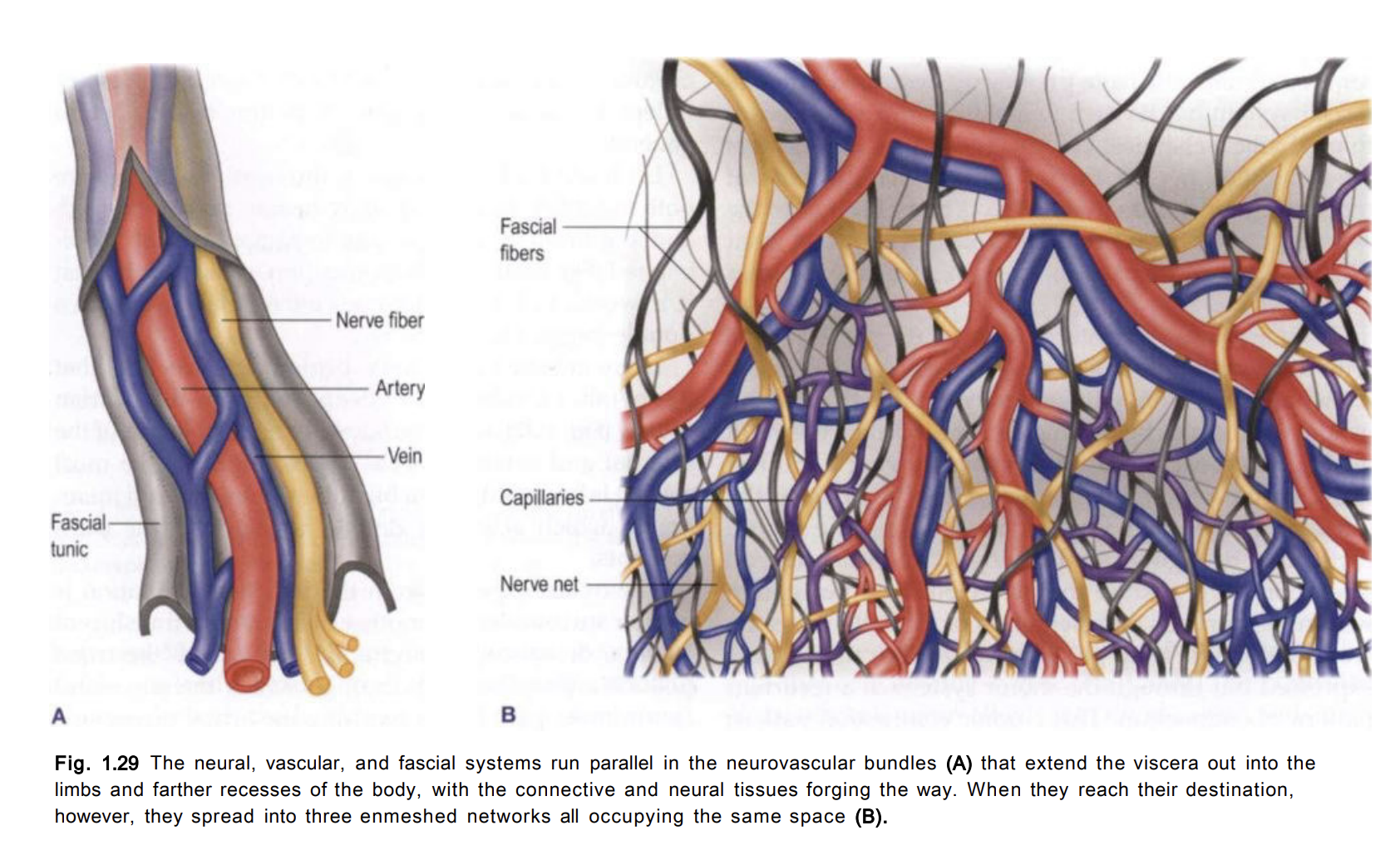
A tight muscle is a(n energetically) weak muscle
Muscles become tight when they are weak and starved of energy, such as during cramps and rigor mortis. Although it seems like a paradox, a strong and healthy muscle is going to be soft to the touch. Remedying your tight muscles is a matter of restoring their metabolism.
Muscles need energy to relax
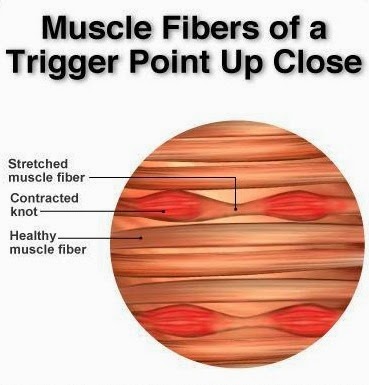
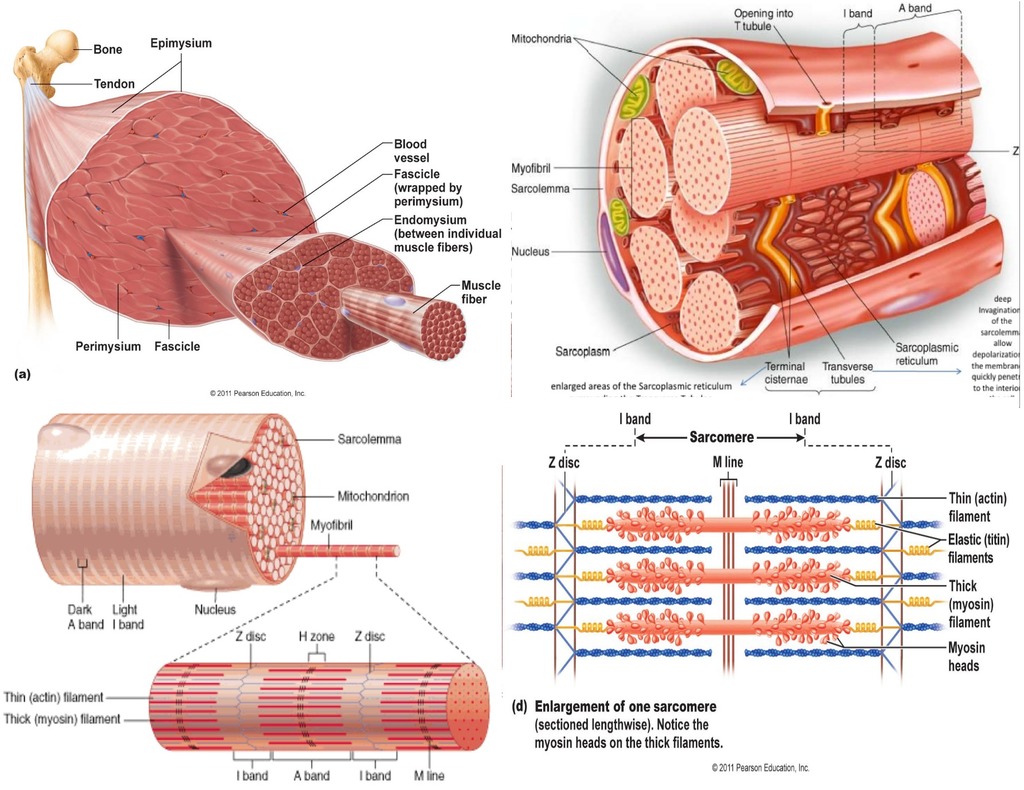
ATP is required for the myosin heads within muscle fibers to detach from the actin filaments. When there is a shortage of ATP, the myosin can remain fixed to the actin, potentially causing the whole muscle to remain in a predominantly contracted state. Usually this occurs in small areas throughout a given muscle and even muscle fibers. This prevents the muscle, as a whole, from being able to relax and contract properly.
Energy (mineral) deficiencies
Deficiencies/imbalances in key minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium can contribute to this. However, anything that influences ATP production will have an effect. These issues become magnified when the muscle is under stress or is worked beyond its capacity. This is why minerals, glucose, and water are a common remedy for cramping during sports.
Stretching and massage: a temporary solution
The common solution is to stretch, massage, or release the muscle in question. This can provide short-term relief but does not solve the underlying issue. If the patterns and circumstances that led to the deficiency in energy are not remedied, then tightness will likely return. That said, stretching and/or massage can still be utilized to encourage the remetabolization of a given muscle or muscles.
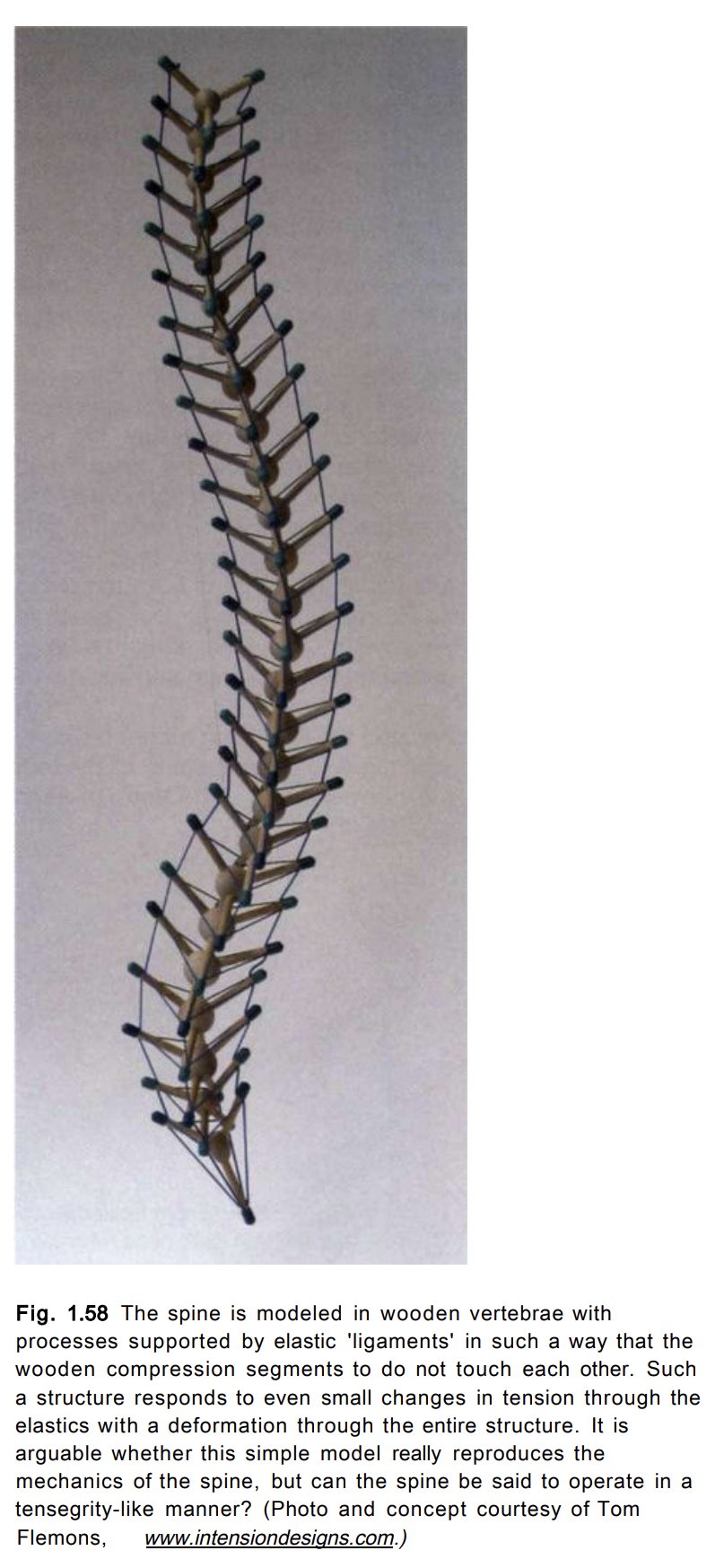
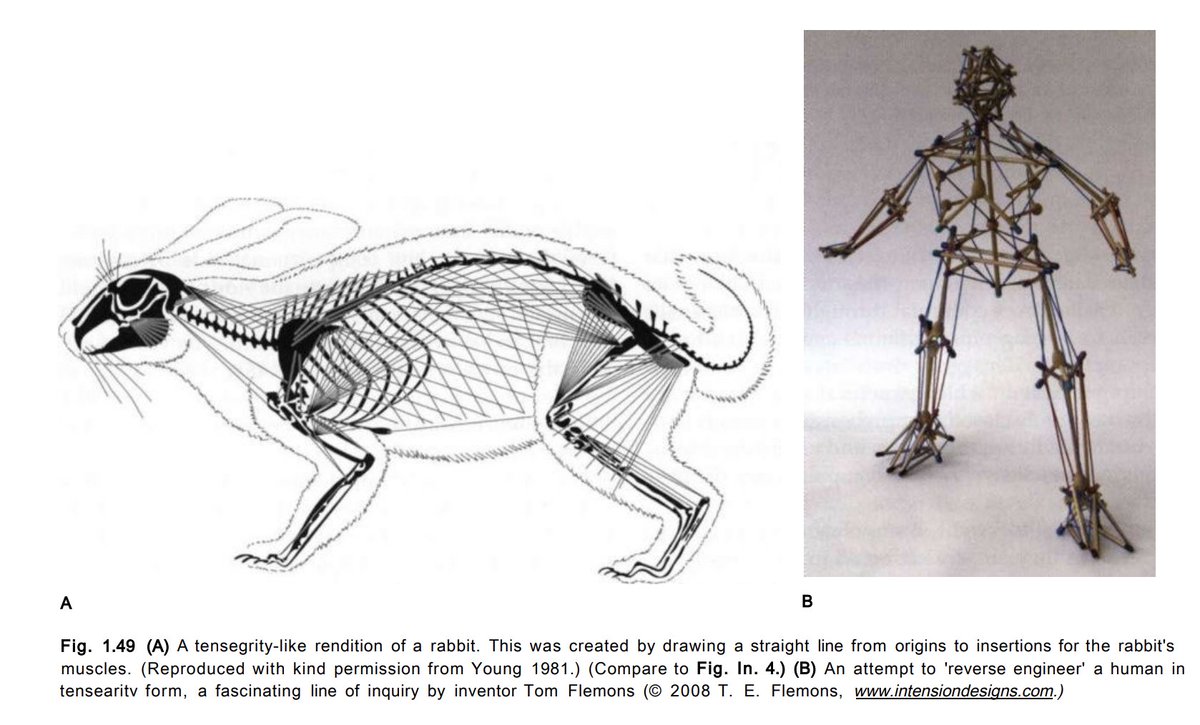
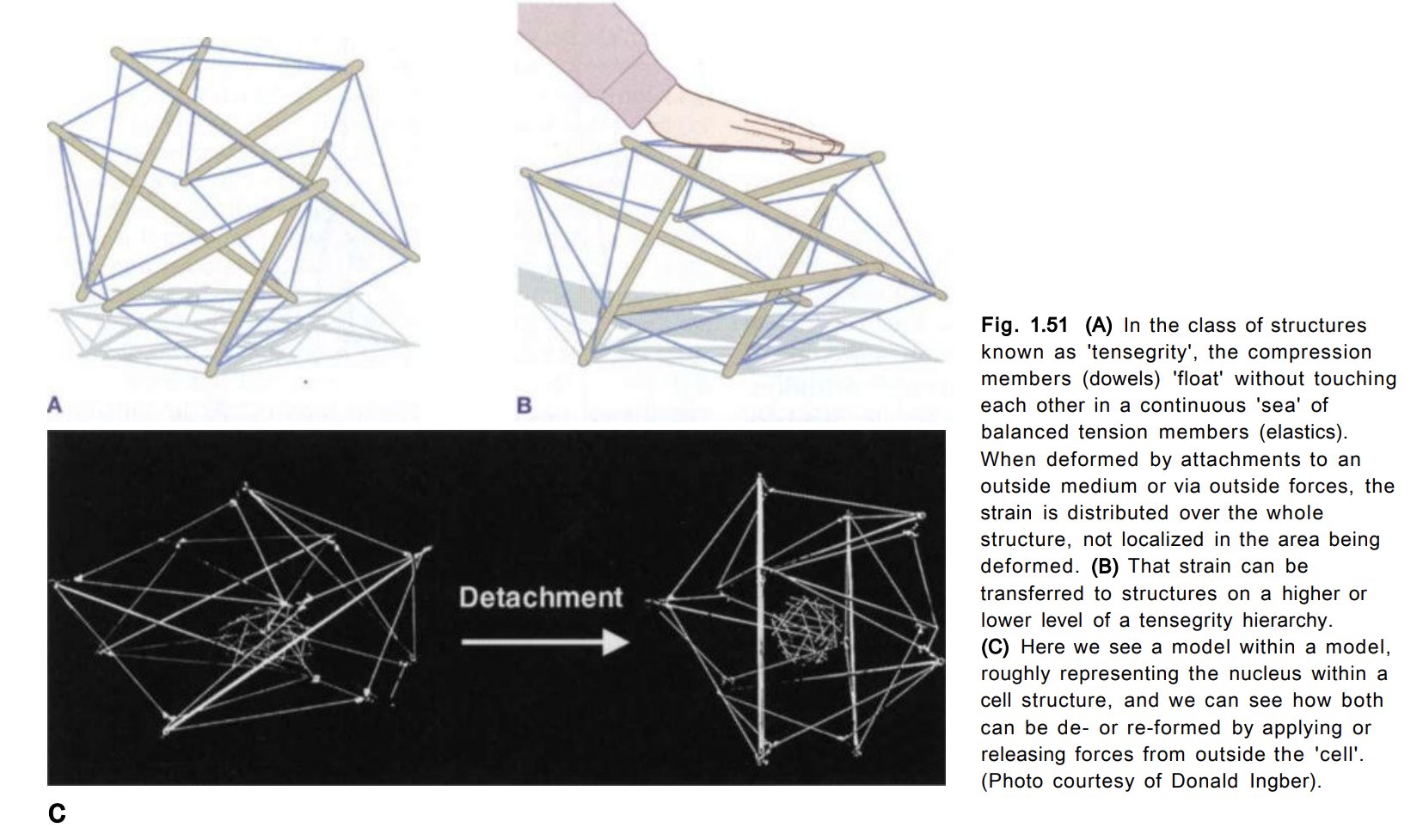
Living tensegrity
Muscle and fascia form a living tensegrity structure that facilitates movement and stability. If you were to push on this structure, the area that ends up enduring the most stress is usually somewhere else along its length. Tight muscles may not be where the problem is occurring.
Pushed beyond their limits
Most chronically tight muscles are those that are being asked to do more than they are metabolically capable of. This either means they are performing a role they are not designed to do and/or don’t have the energy to do so. Usually, these issues go hand in hand. A muscle that is overworked will constantly be burning through energy at a rate it was never designed, continually contributing to its lack of energy.
The dysfunction cascade
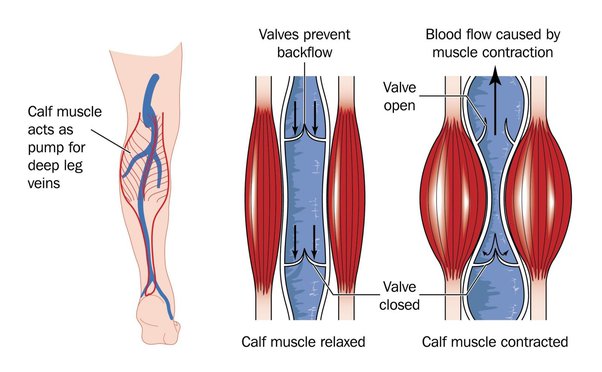
Again, referencing the moving tensegrity structure, drastic alterations to its position will be compensated somewhere else. This area of stress usually experiences increased energy demands while also undermining restorative mechanisms such as the flow of body fluids. A positive feedback loop can ensue, limiting nutrition/energy as the muscle(s) continue to weaken.
Struggling against the nature of things
The connections of muscles, fascia, and the nervous system are constantly working (as one) to keep you upright, moving, and stable. Trying to force a muscle to relax is to struggle against your entire body and can sometimes be detrimental. Tight muscles are usually adaptations that will not go away until the bigger problems are addressed.
A canary in the coal mine
Instead, a tight muscle should be seen as a canary in a coal mine for some form of dysfunction in your body. Addressing fundamental aspects of your existence will drive more (lasting) change than focusing on specific areas of discomfort ad infinitum.
Potential Causes
What can lead to tight muscles?
-Misaligned cranial bones
-Chronic hyperventilation
-Inefficient spinal engine
-Asymmetric postural habits (eyes, tongue, spine)
-Traumatic injuries
-Deficient thyroid metabolism
-ANS dysfunction
-Gut irritation
-Anything that impairs metabolism
Potential Solutions
What are some ways to help restore metabolism to tight muscles?
-Light (infrared)
-Adequate nutrition (sugar, salts)
-Topical nutrition
-Targeted massage/acupressure
-Low-intensity movement
-Microcurrent therapies such as SCENAR
-Grounding/PEMFs
-CO2 baths
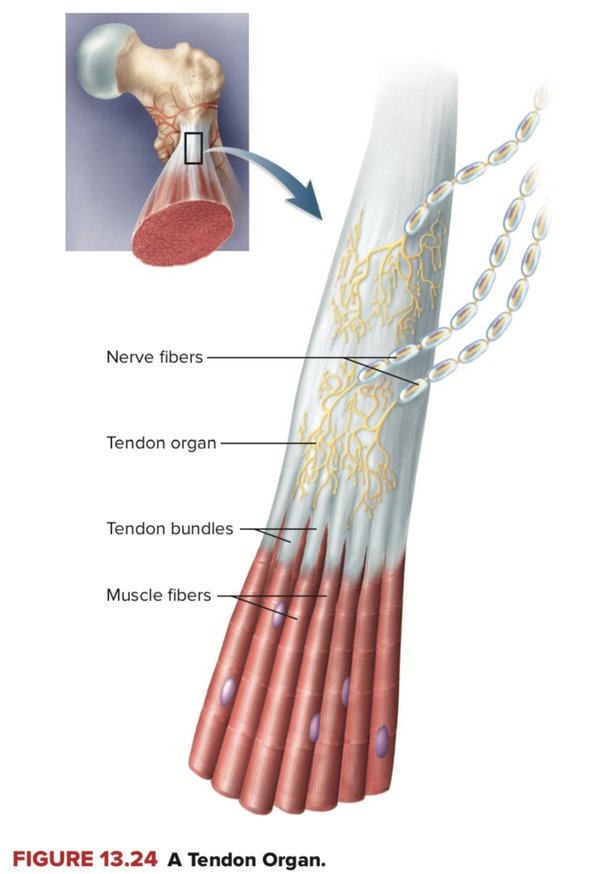
Muscle release
If you are in dire need of a muscle release, you can target the bundles of sensory cells known as Golgi tendon organs. These are located within musculotendinous junctions and can cause muscle cells to relax when stimulated. Gentle massage is all that is required.